Clinical Applications for CBD
There are a host of reported clinical applications for CBD, many of which are for conditions that currently have no effective, or affordable, pharmacological solutions, and/or for which highly addictive opiates and other painkillers are the only known relief. In addition to shining a beacon of hope on treatment of painful or disruptive conditions like many autoimmune and nervous system disorders, CBD bears enormous value as a non-addictive pain relief therapy.
But don’t take our word for it. There is a significant body of scientific evidence detailed in academic and scientific publications, including the Journal of Neurophysiology, Molecular Pharmacology, Neuroscience and Nature, that shows that the human body is engineered to reap the benefits of CBD. The discovery of the endogenous cannabinoid system (ECS) in the 1980s revealed a network of receptors located throughout the body, in the brain, organs, connective tissues, glands, and immune cells. The purpose of these receptors is to achieve homeostasis, a biologic environment that remains stable no matter what external influences exert themselves. Cannabinoids, including CBDs, are made to attach to these receptors.
The absence of a blood-brain barrier in the ECS makes it physically impossible to overdose on cannabis, making its analgesic properties particularly valuable in light of a medical environment where prescription drug abuse for the treatment of pain has reached epidemic proportions.
The ECS can influence a variety of physiological processes including appetite, pain sensation, mood and memory, and in tempering cannabis’ psychoactive impact. Complementing this functionality, CBD has been shown to possess potent anti-tumoral, antioxidant, anti-spasmodic, anti-psychotic, anti-convulsive, and neuroprotective properties, in addition to the ability to fire serotonin receptors, causing an anti-depressant effect. Specifically, the International Cannabinoid Research Society (ICRS) has uncovered numerous molecular pathways through which CBD has great therapeutic potency. Metaphorically, the ECS is the yin to CBD’s yang – the system is made to process CBD (and other cannabinoids) and CBD’s healing powers are expressed through the ECS.
For an overview of the clinical effects of the most prevalent cannabinoids in the Cannabis family, see the chart below. CBD (the blue column), is Cannabinoid Creation’s sole and exclusive focus and yields 16 documented clinical benefits and no psychotropic effects; relief without the “high” or any spaciness or memory loss.
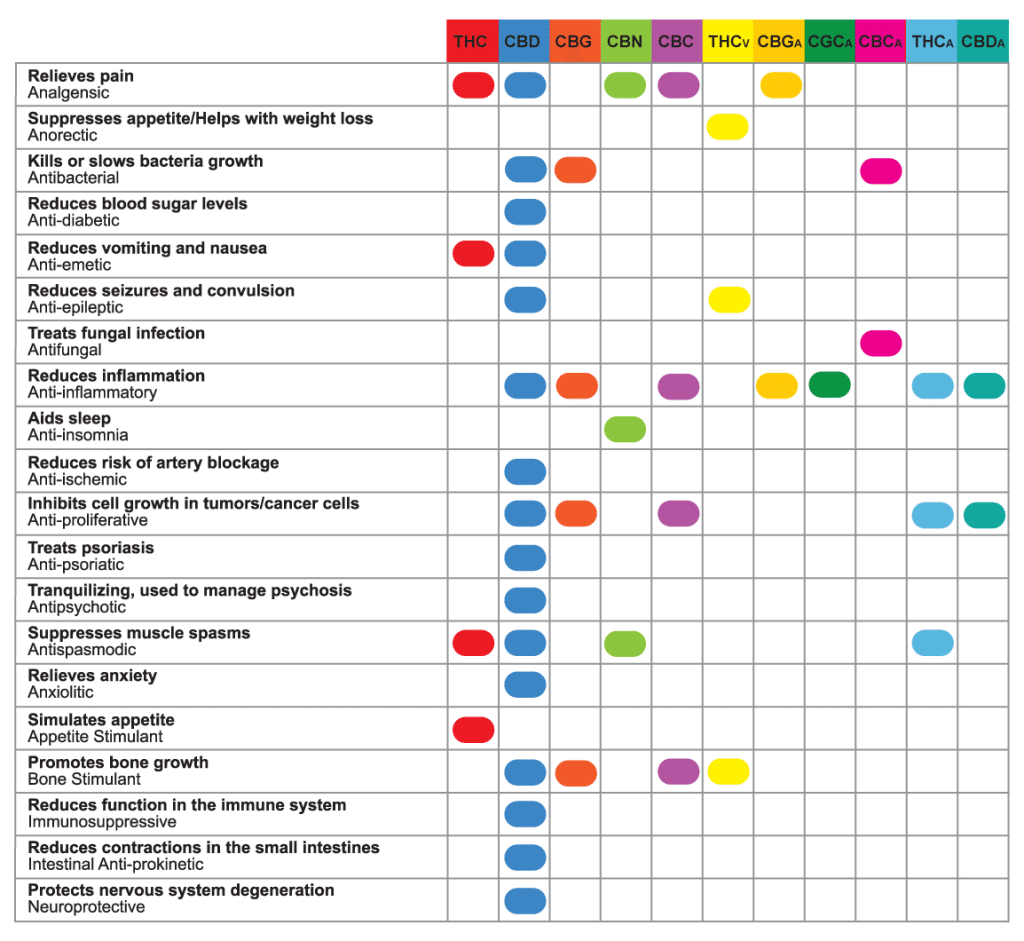
Chart by Media Leafhead


No Comments